
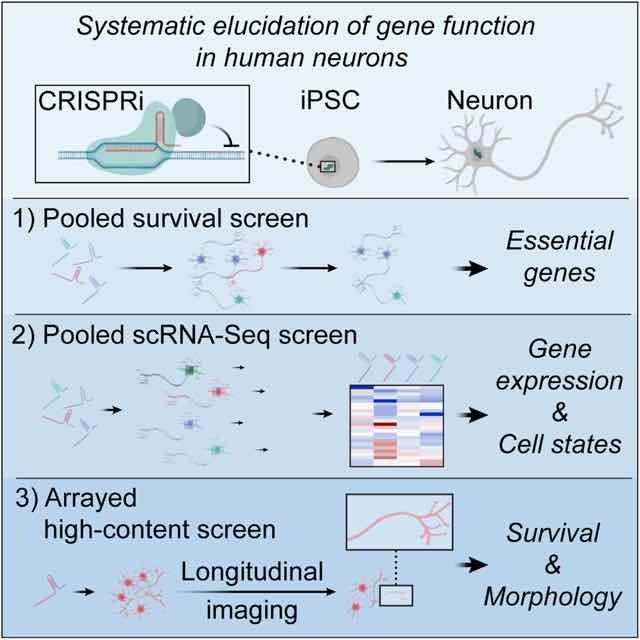
We are developing innovative functional genomics platforms by combining CRISPR screening with other cutting-edge technologies including iPSC differentiation, single cell sequencing, automated high-content imaging and in vivo disease modeling. Using these tools, we aim to uncover cellular and molecular mechanisms of human neurological diseases and develop novel therapeutic strategies
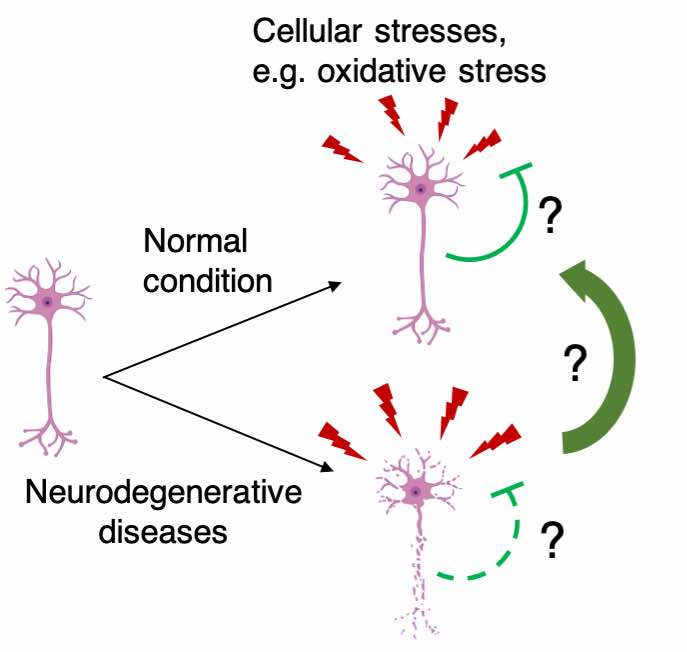
Neurons, as one of the longest-living cell types in the human body, are challenged by various stresses in aging and disease. Due to their post-mitotic nature, neurons do not have the ability to ‘self-renew’ by cell division. Therefore, robust stress response mechanisms are required for neurons to maintain long-term health. We are interested in understanding how neurons response to various cellular stresses in normal and disease conditions and how we could prevent neurons from stress-induced degeneration in diseases. In particular, we are interested in understanding oxidative stress response in neurons and how ferroptosis is regulated in human neurons.
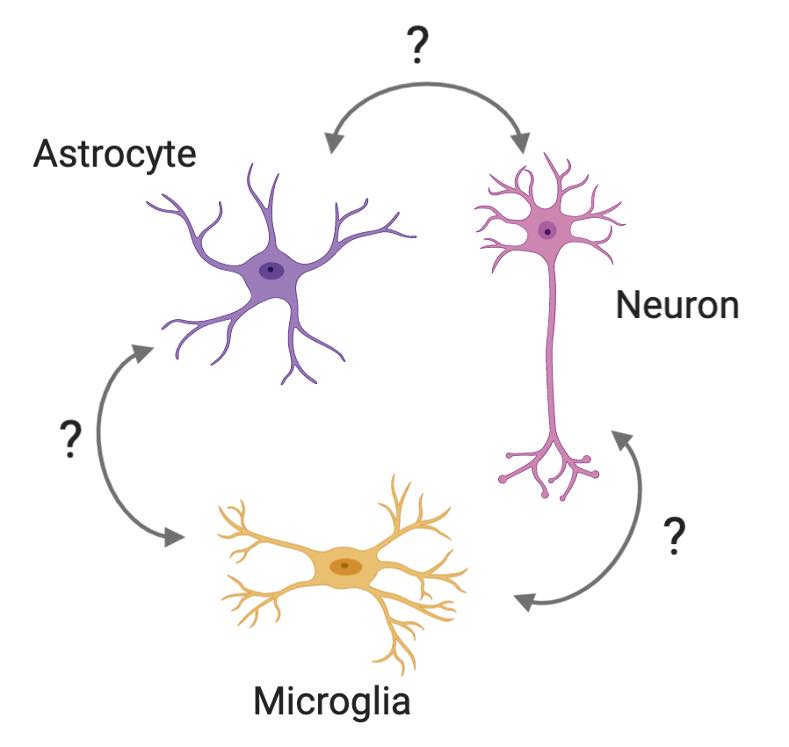
Glia cells, including astrocytes and microglia, play important roles in regulating neuronal survival and supporting neuronal functions. However, under diseases conditions (such as neurodegenerative diseases), glia cells could become neurotoxic. We are interested in identifying key factors that determine the neuroprotective or neurotoxic effect of glia cells to neurons using imaging-based CRISPR screening.
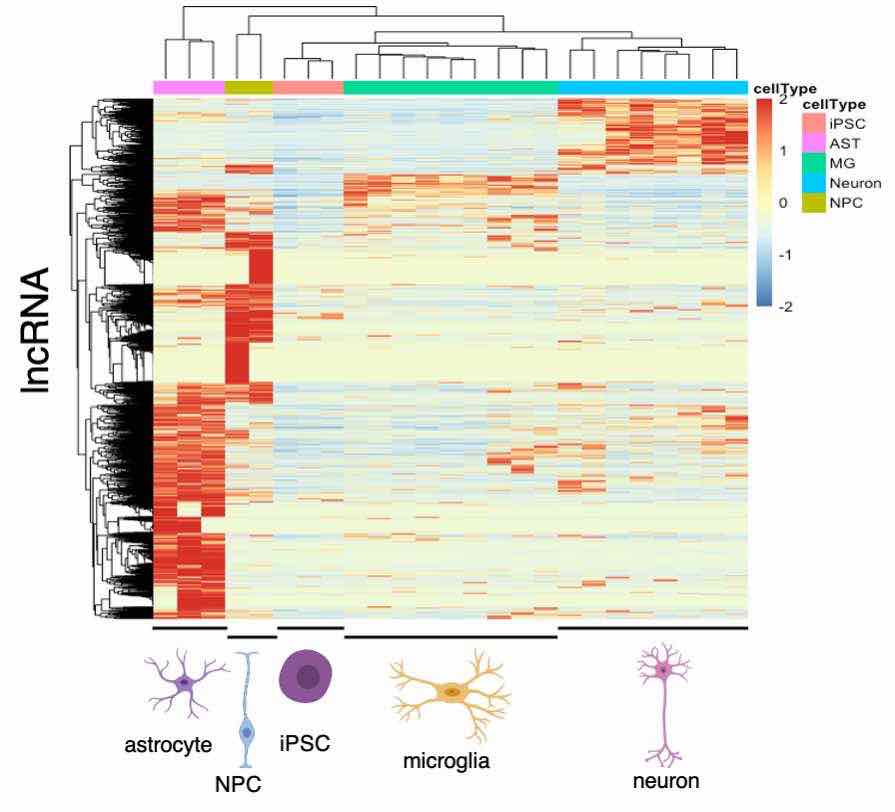
lncRNA are highly tissue-specific and play important roles in regulating various cellular processes. Their functions in human brain cells, including neurons and glia cells, are not well studied. Therefore, we are interested in systematically characterizing lncRNA functions in human neurons, astrocytes and microglia using our CRISPR screening platform.